Mechatronic Systems
Showing 31–36 of 63 results
-

Active flap device for helicopters based on Cedrat Amplified Piezoelectric Actuators
0,00 € Add to downloads -
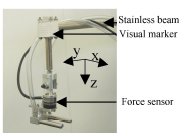
Cardiolock: an Active Cardiac Stabilizer
0,00 € Add to downloads -

LA75B powerful electronic for piezo actuators
0,00 € Add to downloads -

ACTUATOR2008 Moving Iron Controllable Actuators
0,00 € Add to downloads -

ACTUATOR2008 MRF actuators Abstract
0,00 € Add to downloads -

Large Stroke Fast Steering Mirror for Space Free-Space Optical communication
0,00 € Add to downloads


