Publications
Categories
- (34)
- (9)
- (3)
- (143)
- (18)
- (7)
- (4)
- (8)
- (9)
- (17)
- (2)
- (104)
- (7)
- (14)
- (7)
- (1)
- (1)
- (6)
- (155)
- (20)
- (2)
- (5)
- (111)
- (35)
- (11)
- (4)
- (59)
- (18)
- (3)
- (7)
- (62)
- (18)
- (5)
- (24)
- (7)
- (12)
- (1)
- (2)
- (2)
- (1)
- (1)
- (14)
- (13)
- (4)
- (6)
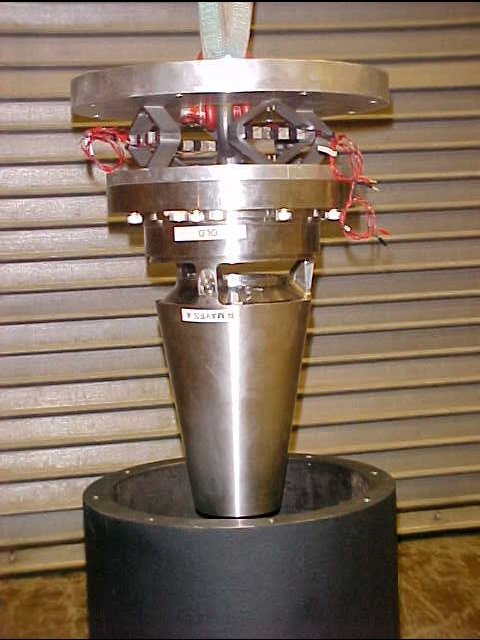

Testing of amplified piezoelectric actuator in a combined vibration and acceleration
19 June 2023
Sandia National Laboratories has previously tested a capability to impose a 7.5 g-rms (30 g peak) radial vibration load up to 2 kHz on a 25 lb object with superimposed 50 g acceleration at its centrifuge facility. This was accomplished by attaching a 3,000 lb Unholtz-Dickie mechanical shaker at the end of the centrifuge arm to create a “Vibrafuge”. However, the combination of non-radial vibration directions, and linear accelerations higher than 50g’s are currently not possible because of the load capabilities of the shaker and the stresses on the internal shaker components due to the combined centrifuge acceleration.

The design and qualification of the piezo actuated
19 June 2023
As part of the Lisa Technology Package (LTP) on board the LISA-PATHFINDER spacecraft, the LISAPATHFINDER interferometer is of the heterodyne Mach-Zehnder type. It requires as input two light beams derived from the same source but with a small frequency difference (a few kHz). These two optical beams are produced in the Laser Assembly (LA) via the “Laser Modulation Unit” (LMU). The LMU includes an optical bench, two Acousto-Optic Modulators and two Optical Delay Lines [1].
Thermal vacuum behaviour of a stepping piezo actuator
19 June 2023
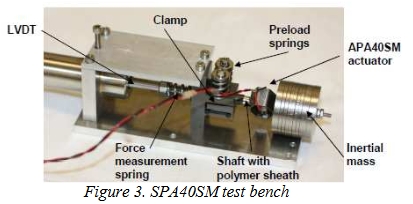
The presented work illustrates the design of a new high force Stepping Piezoelectric Actuator (SPA) and describes its Thermal Vacuum testing as performed by ESTL, in order to investigate SPA compatibility with vacuum environment within a wide temperatures range; from +60°C down to -180°C. A dedicated test bench was designed, in order to check motor force and speed for all performed tests. Instrumentation, testing and observations about tribological behaviour of friction interface have been realized by ESTL, showing interesting perspectives.
Rotating piezoelectric motors for high precision positioning & space applications
19 June 2023
Piezo-electric motors have been successfully developed for various applications like autofocus drives in camera lenses and handling equipment for semiconductor production. Their high speed and accurate positioning capability, combined with a favourable holding torque in unpowered condition, make piezomotors also very attractive for actuation purposes in spacecraft mechanisms. The paper introduces a new concept of a versatile ultrasonic piezomotor. The testing campaign carried out on the designed rotating piezomotor has validated the vacuum compatibility and the lifetime of the motor in air.

Rotating step by step piezomotor for nanopositioning and space applications
19 June 2023
Piezomotors are well known in various applications where high precision actuation is required like AFM or handling equipment for semiconductor production. Their specific low speed in direct drive and high torque characteristics combined with high holding torque in off power conditions make them very attractive for any positioning application and especially space mechanisms where low electrical consumption is always sought. A new concept of rotating stepping piezomotor has been developed in the frame of the LISA space project where the mechanism of the telescope orientation was addressed.

Rotation free linear actuator
19 June 2023
This paper presents the development of a rotation free linear actuator: The use of highly dynamic actuator in the rotating frame, such as piezo actuator, required dedicated devices to transmit the electrical power from the static frame to the rotating one. Slip rings and rotating transformers are able to provide this function. However the integration of such components required invasive operations


