Publications
Categories
- (34)
- (9)
- (3)
- (143)
- (18)
- (7)
- (4)
- (8)
- (9)
- (17)
- (2)
- (104)
- (7)
- (14)
- (7)
- (1)
- (1)
- (6)
- (155)
- (20)
- (2)
- (5)
- (111)
- (35)
- (11)
- (4)
- (59)
- (18)
- (3)
- (7)
- (62)
- (18)
- (5)
- (24)
- (7)
- (12)
- (1)
- (2)
- (2)
- (1)
- (1)
- (14)
- (13)
- (4)
- (6)

Design of a 2 stages compressor for mobility applications, using compact and efficient Moving Iron Controllable Actuators
19 June 2023
An actuator is rescaled for integration into a compressor used for the liquefaction of hydrogen vapor boil off, into a propellant storage system. The goal is to evaluate the feasibility of liquid hydrogen zero boil off, for long duration storage at 20 Kelvin cryogenic liquid condition. This article presents the actuator trade off, selection and special features imposed by the application. The actuator design is presented, its characteristics are measured, and resulting performances are presented and discussed.
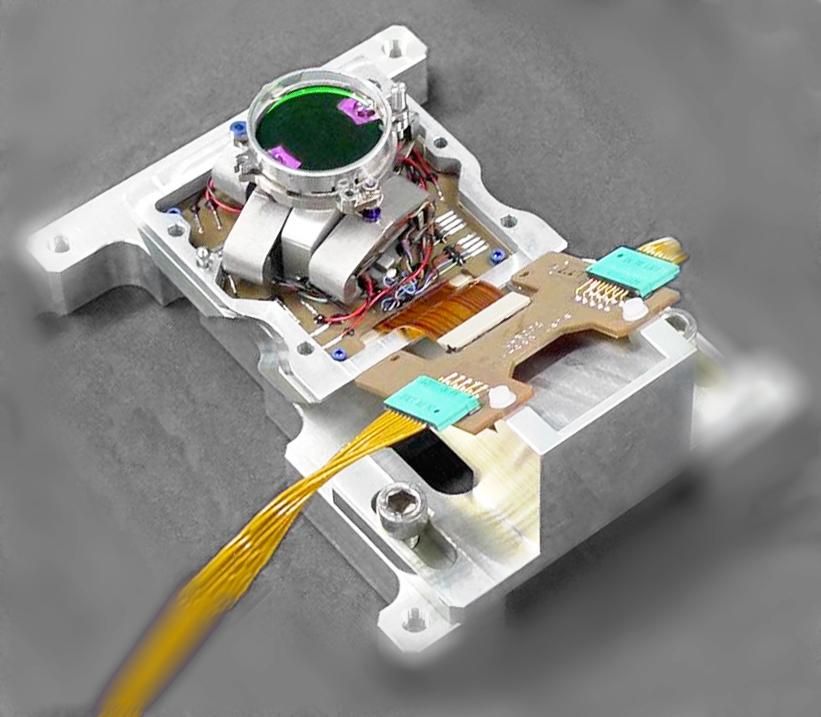
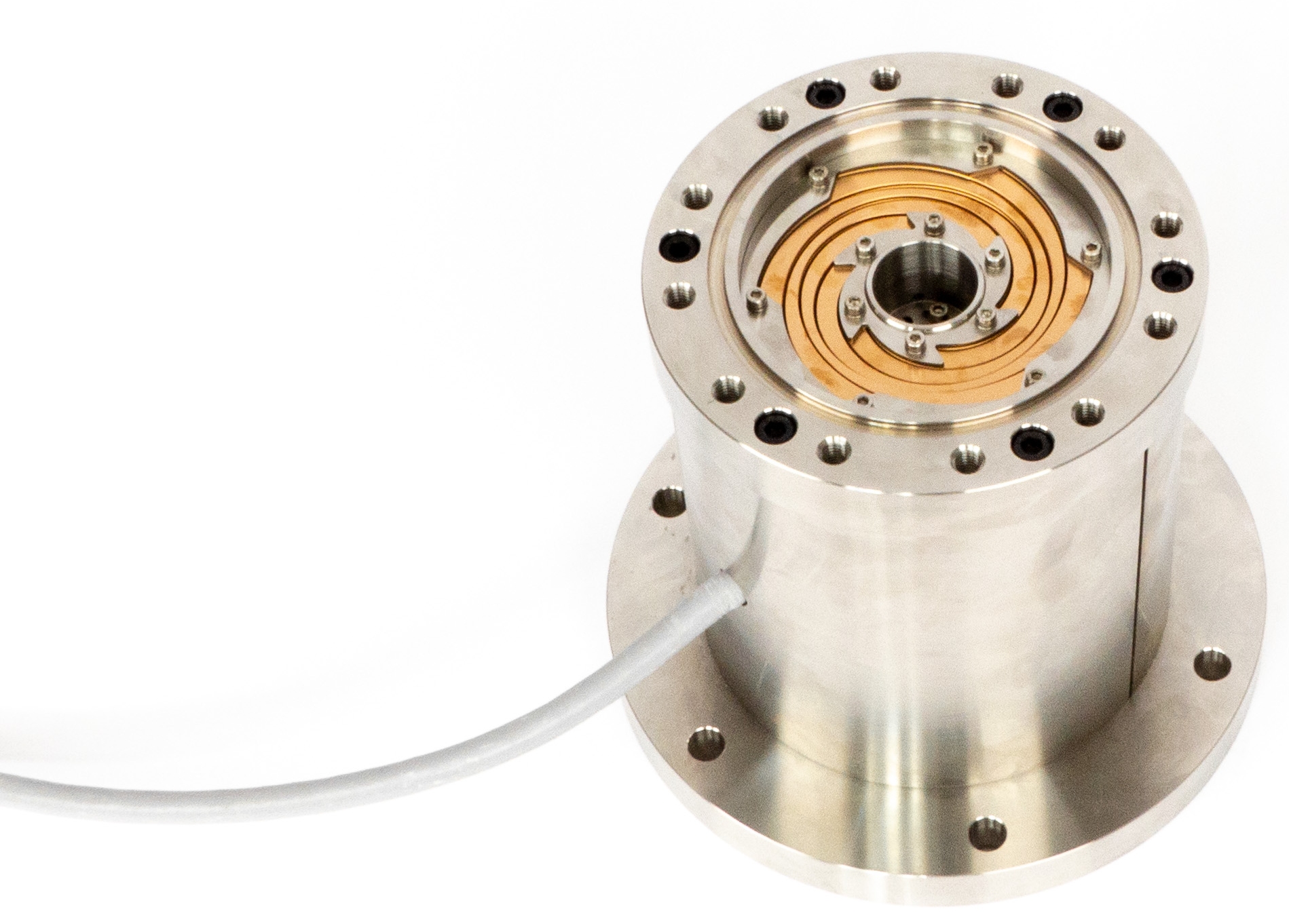
ATLID BSA Beam steering assembly piezo tip tilt
19 June 2023
ATLID (ATmospheric LIDar) is one of the four instruments of EarthCARE satellite, it shall determine vertical profiles of cloud and aerosol physical parameters such as altitude, optical depth, backscatter ratio and depolarisation ratio. The BSA (Beam Steering Assembly), included in emission path, aims at deviating a pulsed high energy UV laser beam to compensate the pointing misalignment between the emission and reception paths of ATLID [1]. It requires a very high stability and high resolution.

Beam steering mechanism for earthcare atmospherice Lidar Instrument: an improved piezo tip-tilt mechanism
19 June 2023
In the context of the ATLID instrument [1] embedded in the EarthCARE mission (Earth Cloud, Aerosol and Radiation Explorer), a Beam Steering Assembly is deviating a pulsed high energy UV laser beam to compensate the pointing misalignment between the emission and reception paths of ATLID with a very high stability and high resolution. Within the EarthCARE mission, led by ESA, Astrium is responsible for the ATLID instrument. The BSA development, manufacture and tests were assigned by Astrium to Sodern, an EADS filial.

Beam steering mirrors: from space applications to optronic applications
19 June 2023
Fast growing Laser and new optic applications drive more and more needs for beam steering mirrors (BSM) and Fast Steering Mirror (FSM). For space optic instruments, CEDRAT TECHNOLOGIES has developed for 20 years several piezoelectric tip-tilt mechanisms. Presented recent examples include the ATLID BSA small tit tilt for quasi static nano pointing and MEFISTO, a large tit tilt for fast micro positioning. These space mechanisms perform high precision functions while being compact, lightweight and resistant to external vibrations and shocks. As shown in the paper, these advantages allow these technologies addressing several needs for other optronic applications than space, such as active stabilisation, micro scanning, disturbance compensation in IR imagers or telescopes.

Benefits from amplification of piezo actuation in inertial stepping motors
19 June 2023
Stepping Piezo Actuators (SPA) are long stroke linear piezoelectric actuators capable to reach long stroke (typ. >10mm) with an important resolution (typ. <1nm). It has been proposed to use Amplified Piezo Actuator into inertial stepper motor to build the SPA. This piezo motor showed good behaviour, with relatively high speed (up to 70mm/s), force (from 0.2N to 20N) and low consumption (down to 700mW).

Bistable micro actuator for energy saving
19 June 2023
The article describes a linear magnetic flip-flop micro actuator, designed with FLUX software, assembled and characterised for a specific application requiring low losses at function states. The micro size allows reducing the energy required for actuation. Permanent magnets ensure bistability and suppress losses at functional states. Although the actuator is less than 1 g, the blocking force is about 0.1N and the stroke is 0.6mm. Firstly, the paper describes the main functionality of the actuator. Then are presented measured characteristics and results are compared with FLUX software computation. Finally perspectives of further miniaturisation are discussed.


