Publications
Categories
- (34)
- (9)
- (3)
- (143)
- (18)
- (7)
- (4)
- (8)
- (9)
- (17)
- (2)
- (104)
- (7)
- (14)
- (7)
- (1)
- (1)
- (6)
- (155)
- (20)
- (2)
- (5)
- (111)
- (35)
- (11)
- (4)
- (59)
- (18)
- (3)
- (7)
- (62)
- (18)
- (5)
- (24)
- (7)
- (12)
- (1)
- (2)
- (2)
- (1)
- (1)
- (14)
- (13)
- (4)
- (6)
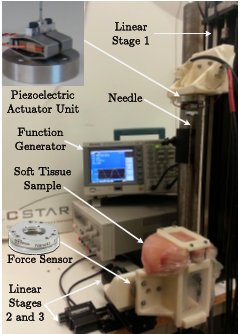
Analysis of Needle–Tissue Friction during Vibration-Assisted Needle Insertion
19 June 2023
In this paper, a vibration-assisted needle insertion technique has been proposed in order to reduce needle–tissue friction. The LuGre friction model was employed as a basis for the current study and the model was extended and analyzed to include the impact of high-frequency vibration on translational friction. Experiments were conducted to evaluate the role of insertion speed as well as vibration frequency on frictional effects. In the experiments conducted, an 18 GA brachytherapy needle was vibrated and inserted into an ex-vivo soft tissue sample using a pair of amplified piezoelectric actuators. Analysis demonstrates that the translational friction can be reduced by introducing a vibratory low-amplitude motion onto a regular insertion profile, which is usually performed at a constant rate.
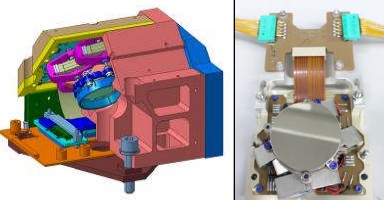
ATLID Beam Steering Mechanism and derived new piezoelectric based devices for optical applications
19 June 2023
In Space & Defence (as well as in many others fields), there is a trend for miniaturisation in active optics requiring new actuators. Applications also often require the ability to withstand high vibrations and shocks levels, as well as vacuum
compatibility for space applications. A new generation of small and smart actuators such as piezoelectric (piezo) actuators, are resolving this trend, thanks to their capacity to offer high energy density and to support both extreme and various requirements. This paper first presents the BSM mechanism and its requirements, the technologies involved in
the design and the validation campaign results. Secondly, a derived XY piezoelectric positioning stage based on the same APA® and associated Strain Gage sensing technology is presented with its associated performances. Finally, a new piezoelectric motor based on the APA® technology, which allows the combination of long stroke while maintaining high
resolution positioning of optical elements, is presented with experimental performances.
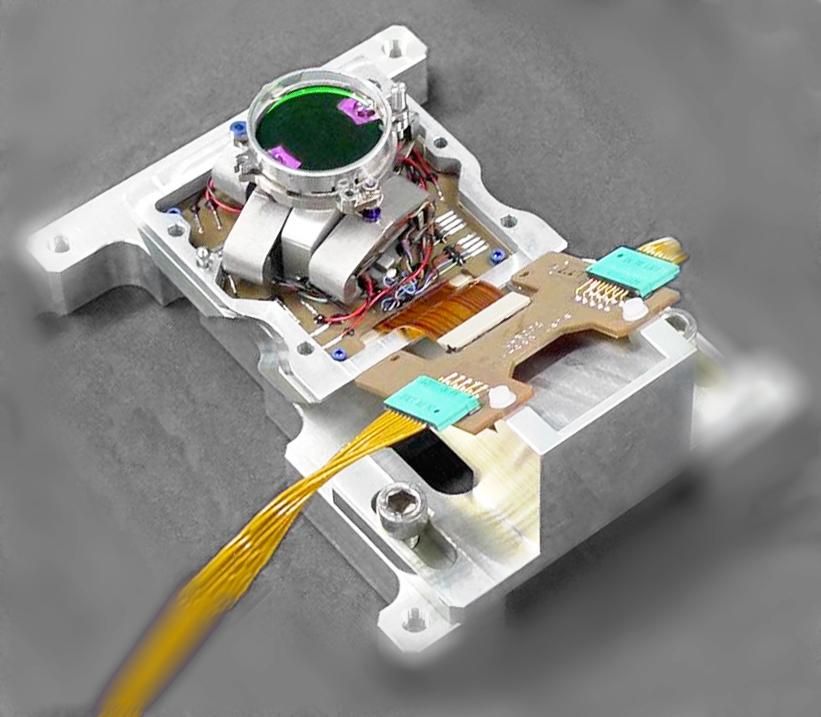
ATLID BSA Beam steering assembly piezo tip tilt
19 June 2023
ATLID (ATmospheric LIDar) is one of the four instruments of EarthCARE satellite, it shall determine vertical profiles of cloud and aerosol physical parameters such as altitude, optical depth, backscatter ratio and depolarisation ratio. The BSA (Beam Steering Assembly), included in emission path, aims at deviating a pulsed high energy UV laser beam to compensate the pointing misalignment between the emission and reception paths of ATLID [1]. It requires a very high stability and high resolution.
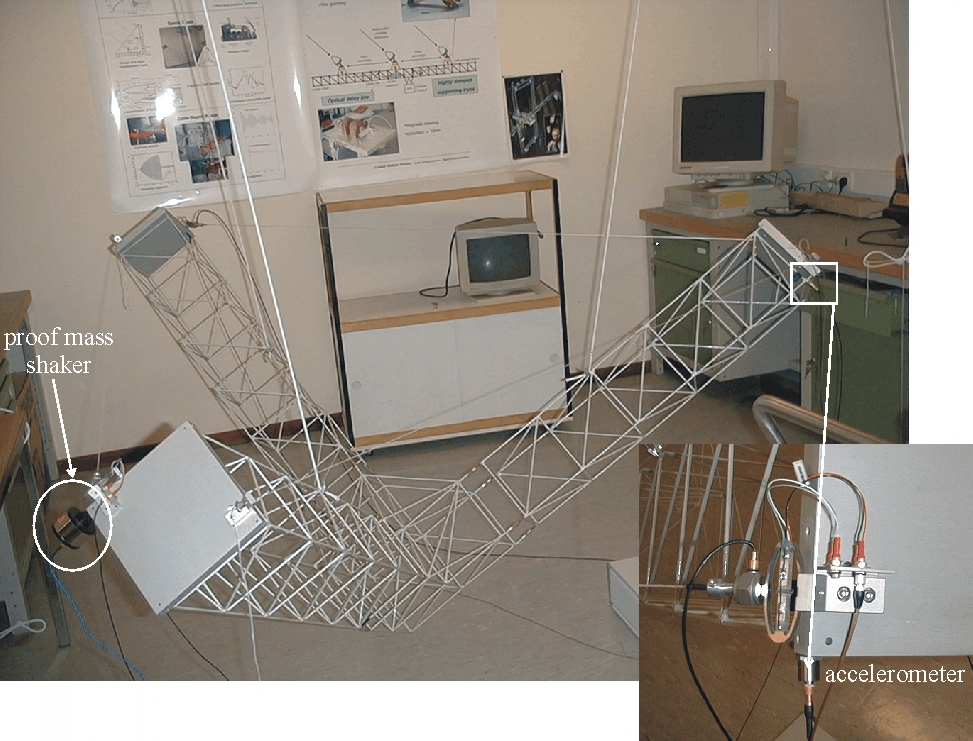

Active control of vibrations of a space truss using amplified piezoelectric actuators
19 June 2023
The new piezo actuators manufactured by Cedrat Technologies have been developed for the positioning control of space optics but they are spreading widely in various engineering fields such as precise positioning, intelligent control of shapes and generation or control of vibrations. Their ability for the control or active damping of vibrations has been successfully demonstrated at the lab scale in space applications. In a first case, the piezo actuators were used for both for the control of launching vibrations and the positioning control in orbit of a telescope mirror. In a second set of space applications, these piezo actuators have been successfully integrated in a space truss using active tendons for control of micro vibrations, as publicly released at the Industry Space Days (ISD2001, Noordwijk, 9-10 Mai 2001) and as presented in this paper.

Active damping of vibrations applied on ski structures
19 June 2023
Since many years the field of active controls of vibration is growing up and a lot of new applications using smart actuators are developed. In the following study, these concepts are adapted and applied on a general structure of ski to damp the large modes of vibrations keeping the robustness of the control and the static loads during the ride.. Simulations integrating FEM models coupling to electromechanical model were elaborated to obtain the principal performances and to study the stability of the loop.

Active flap device for helicopters based on Cedrat Amplified Piezoelectric Actuators
19 June 2023
A project called RPA (Rotor à Pales Actives) was launched three years ago to study the possible benefits of implementing active trailing edge flaps on a helicopter main rotor. The main objectives of this project are to decrease BVI noise in descent flight and improve the dynamic behavior of the rotor throughout the largest possible flight domain. After a first phase dedicated to the design of the best flap configuration at scale 1, the second phase of the project deals with the design of a wind-tunnel scale model of a rotor equipped with active flaps. An off-the-shelf piezo-electric actuator is used together with a specific patented flap-driving mechanism. Such an active device was tested under centrifugal loads as well as under aerodynamic loads in order to prepare future wind-tunnel tests. The results obtained under centrifugal loads allowed to clear the active device but the aerodynamic testing showed that some improvements were needed. Corresponding modifications are under way to fully clear the active device to be used on a complete rotor model.


