Publications
Categories
- (34)
- (9)
- (3)
- (143)
- (18)
- (7)
- (4)
- (8)
- (9)
- (17)
- (2)
- (104)
- (7)
- (14)
- (7)
- (1)
- (1)
- (6)
- (155)
- (20)
- (2)
- (5)
- (111)
- (35)
- (11)
- (4)
- (59)
- (18)
- (3)
- (7)
- (62)
- (18)
- (5)
- (24)
- (7)
- (12)
- (1)
- (2)
- (2)
- (1)
- (1)
- (14)
- (13)
- (4)
- (6)
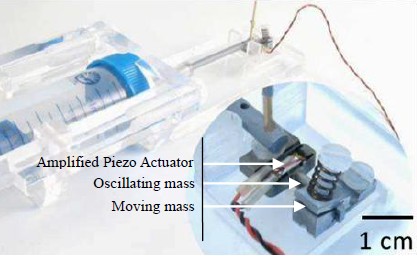
Design of a dynamic tribometer applied to piezoelectric Inertia Drive Motors – In situ exploration of stick-slip principle
19 June 2023
In Inertia Drive Motors, generated motion is based on stick-slip principle. Current analytical models are predictive enough to calculate qualitatively their optimal performances, such as maximal step size and speed, with relatively few input parameters. But, they do not take into account the contact life and temporal evolution of parameters as friction factor all along lifetime of IDM. So, analytical models reach their limits when precise predictions are necessary. This investigation aims at understand wear mechanisms to model temporal evolution of friction. Such an understanding requires the reconstitution of the contact life through the evaluation of 1st and 3rd body flows. To do so, a new IDM-representative tribometer is designed. First bodies – coated TA6V and polymer – are not see-through. They are replaced alternatively by an intermediate transparent first body to observe the contact dynamically and in-situ. Friction factor, step size and mean speed are also measured. Preliminary results shows that wear profiles from real IDM and tribometer are similar. Direct observations bring out particles of TA6V coating are firstly snatched, then moves in contact and finally trigs others particle detachments.

Actuators in adaptronics: piezoelectric actuators
19 June 2023
Piezoelectric actuators have increased their number of application in adaptronics over the past decade [1]. They can be used with several drive and control strategies and they are more adapted to mechatronics applications requiring bandwidth, accuracy and/or lightweightness. The purpose of this paper is to recall the different existing piezo actuators, the different drive and control techniques and finally review several applications in machine tools, optics.

Actuators, transducers and motors based on giant magnetostrictive materials
19 June 2023
Rare earth-iron magnetostrictive alloys, especially Terfenol-D, feature “giant” magnetostrains: static strains of 1000-2000 ppm and dynamic strains of 3500 ppm are reported.
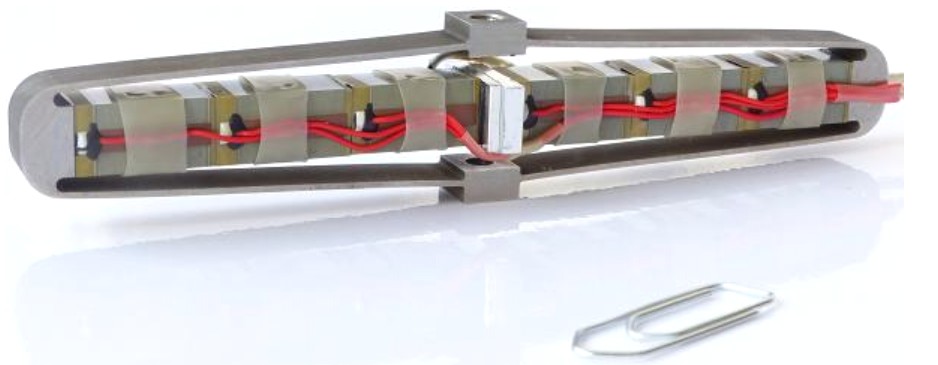
Advantages of large piezo actuators and high power drivers for fatigue and fretting test
19 June 2023
Constant expansion of new materials requires fretting or fatigue machines in order to test their failure. In many cases tests must be performed in severe conditions and at high frequency. These requirements come from the use of the materials in highly demanding applications. At the same time it is expected to reduce the time required to characterise such materials. Piezoelectric actuators are more and more common in testing machines, but they still reach limitations in terms of maximum displacement, cycling frequency or power. In order to cope with these issues, Cedrat Technologies has been investigating solutions. In this paper long stroke and high frequency actuators, coupled with powerful driving control are introduced. These actuators are based on piezoelectric materials and can be easily integrated into the fatigue machines. In order to improve precision of these tests, two of the most common displacement sensors used in smart actuators are also presented in this paper.
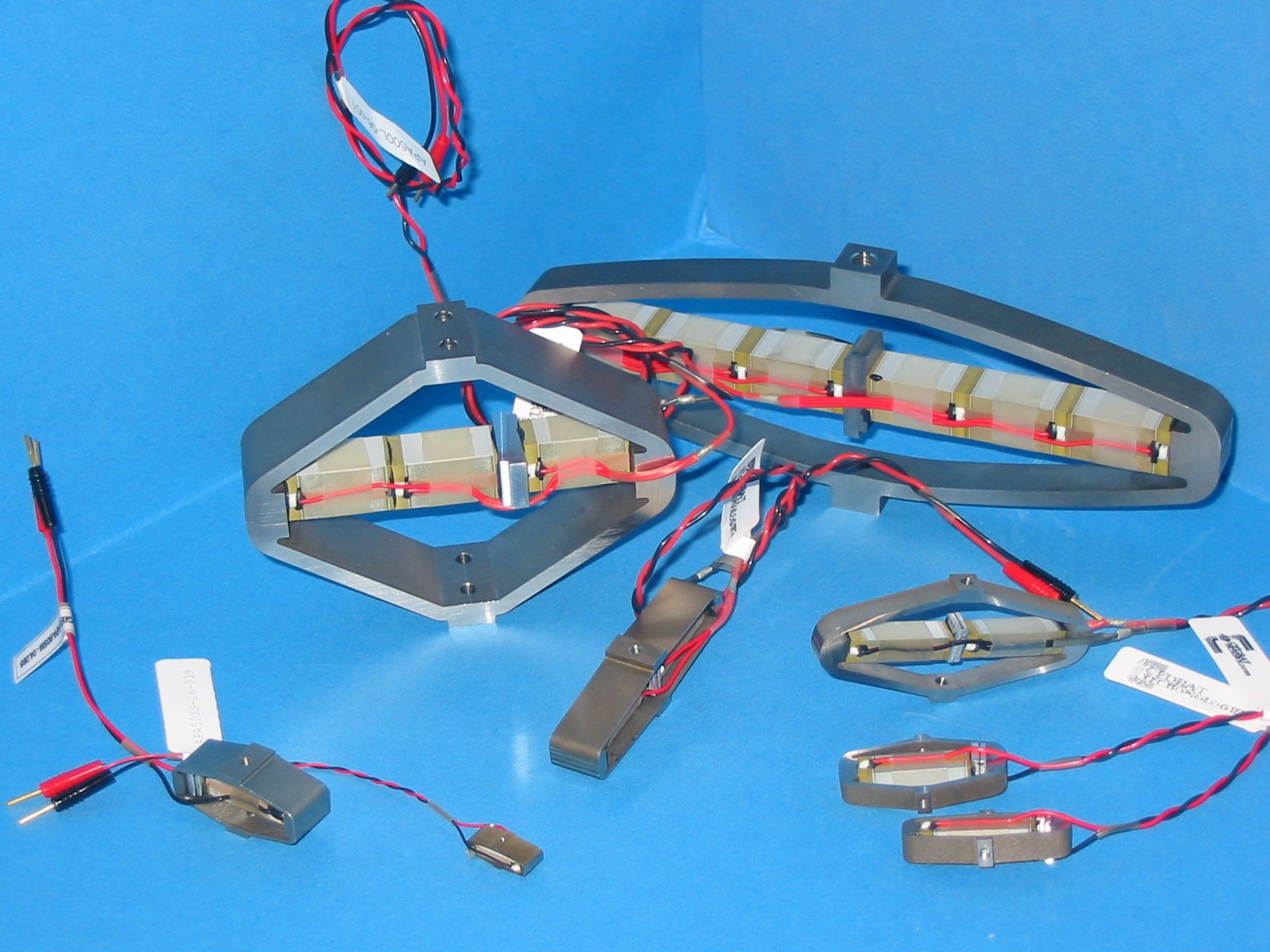
Aero India 2003 Piezo actuators air & space
19 June 2023
Several classes of Piezo Actuators based on low voltages piezo ceramics have been developed by CEDRAT TECHNOLOGIES in order to cover needs for long stroke, precise and/or fast positioning in the fields of air & space applications. A specific class of Amplified Piezo Actuators, so called APA has been patented, developed and qualified. Their applications concern subjects as various as Scientific Instruments for Space payloads (Telescopes, Microscopes), Micro-Satellites Propulsion Valves or Active flaps of Helicopter Blades.

Amélioration des performances des actionneurs APA®
19 June 2023
Increase the dynamic mass energy density and reduce the effects of inertia by playing on materials and geometry.


