Cedrat Technologies at the heart of the LISA project, the future flagship mission for gravitational wave observation
Cedrat Technologies (CTEC), a specialist in piezoelectric actuators and motors for extreme environments, announces its contribution to the LISA (Laser Interferometer Space Antenna) project, one of the most ambitious scientific space missions ever launched in Europe.
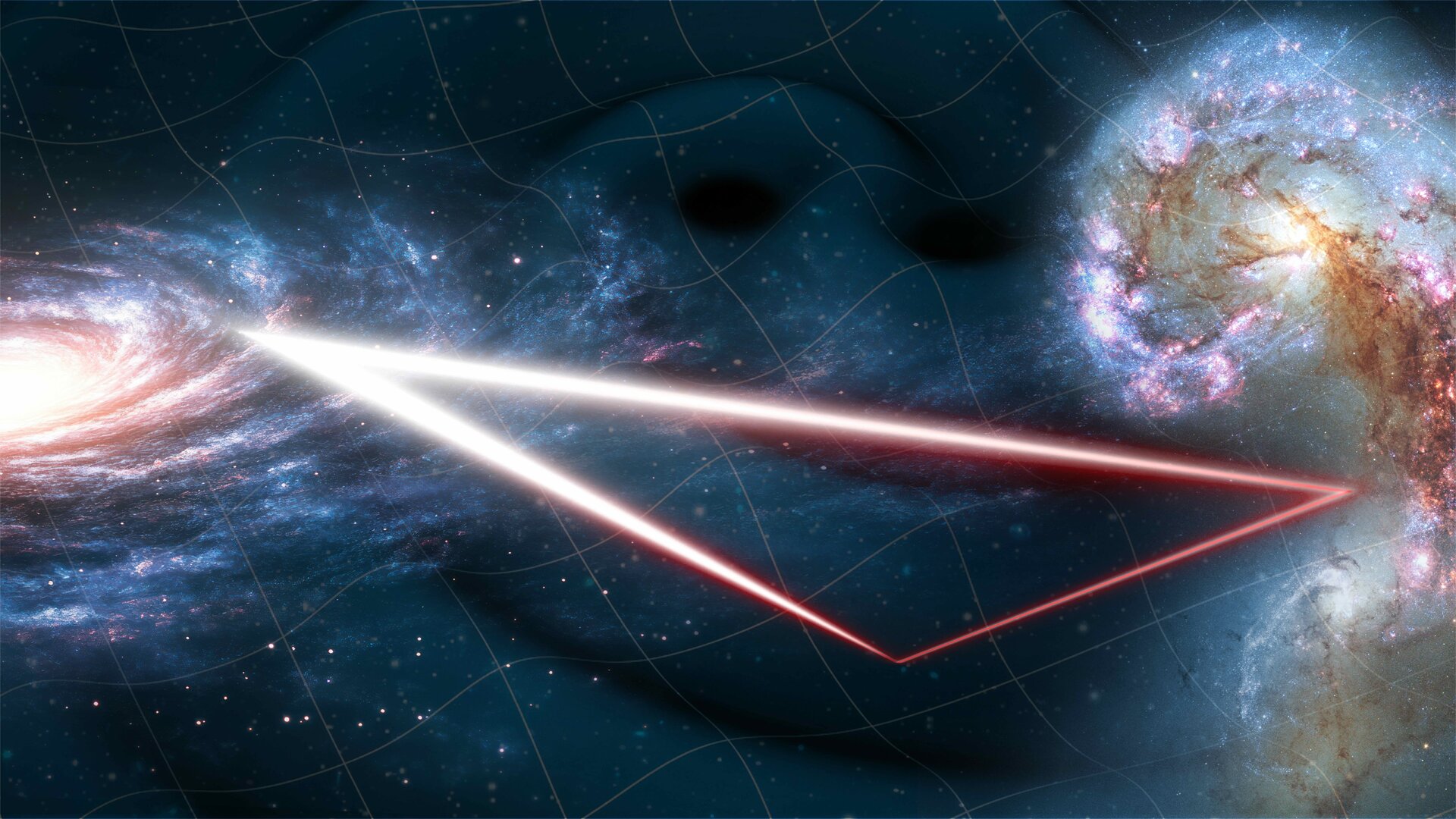
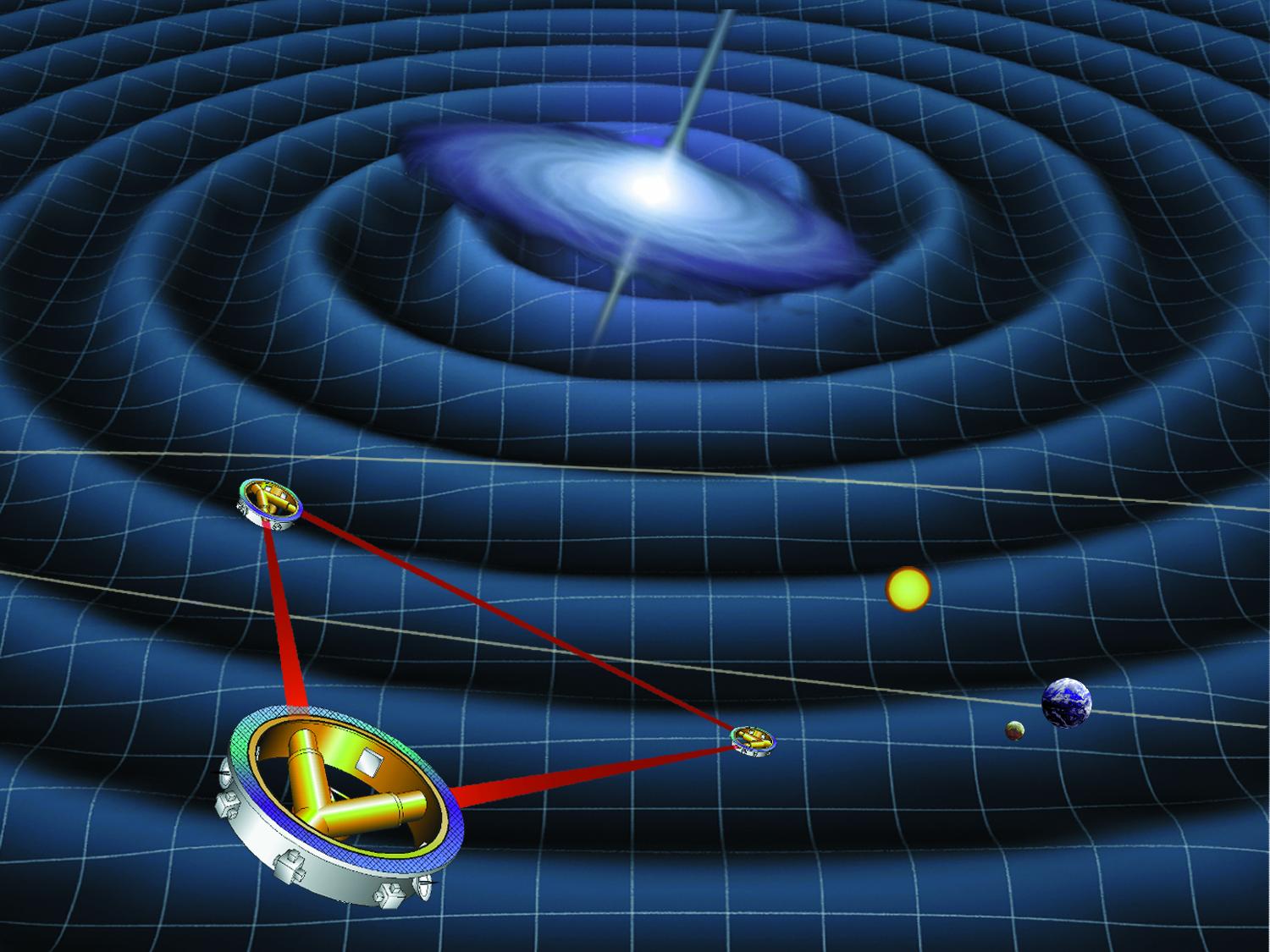
Led by ESA and NASA, with the contribution of CNES, the LISA project represents an investment of more than €1 billion. This L-class mission, ESA’s third “Large” mission, aims to become the first space observatory dedicated to the detection of gravitational waves, opening a new window for observing the Universe.
Time-lapse of the motor intended for the Antenna Pointing Mechanism (APM).
Key piezoelectric expertise for an extraordinary mission
The LISA mission will rely on a constellation of three satellites forming a triangle with sides measuring 2.5 million kilometers, flying in extremely precise formation. In this context, the onboard mechanisms must meet unprecedented requirements: ultra-low micro-vibrations, exceptional magnetic cleanliness, and extreme angular resolutions.
Cedrat Technologies is involved in several European consortiums to develop very high-resolution piezoelectric rotary motors suitable for critical mission functions. This work has enabled TRL 3 (Technology Readiness Level) to be achieved on custom-built motors dedicated to LISA.
These developments include:
- A motor for the Antenna Pointing Mechanism (APM) of the high-gain antenna, capable of continuous rotation of 1° per day without interrupting scientific observations, with a positioning accuracy of ±0.05° over 360°
- Motors for the Optical Assembly Tracking Mechanisms (OATM), ensuring optical alignment between satellites with microradian precision, then nanoradian stability in cooperation with the DFACS system.
- Beam alignment micro-motors (BAM), designed for use in the optical bench to correct for parasitic variations in the optical path length by laterally shifting the transmitted beam.
These performances demonstrate the potential of “inchworm-type” piezoelectric motors for extremely demanding space applications.
A "wonderful industrial story" in the service of space exploration
Cedrat Technologies’ involvement in LISA is part of a long-standing relationship with the French and European space sector:
1995
CTEC begins R&D work on piezoelectric actuators for CNES.2018
Delivery of BSMA linear piezo motors in flight models for the IASI-NG mission, for ADS and CNES, now in operation on METOP satellites.2022
Completion of initial feasibility studies for piezoelectric rotary motors for LISA, with support from Bpifrance as part of the PROOFED program.
2024
Winning three major projects for the development of piezoelectric motors for LISA, as mentioned above, representing a cumulative order value of over €10 million.
contributing directly to major European scientific missions.
Learn more about LISA
LISA (Laser Interferometer Space Antenna) is a European scientific mission dedicated to observing gravitational waves from space. It will enable the study of major astrophysical phenomena such as the merger of massive black holes or the evolution of compact binary systems, which are impossible to observe from Earth.
More information, including infographics, can be found on the following websites:





