Publications
Categories
- (34)
- (9)
- (3)
- (138)
- (18)
- (7)
- (2)
- (5)
- (8)
- (17)
- (1)
- (100)
- (7)
- (12)
- (7)
- (1)
- (1)
- (4)
- (152)
- (19)
- (2)
- (5)
- (111)
- (34)
- (10)
- (4)
- (55)
- (14)
- (3)
- (7)
- (61)
- (17)
- (5)
- (24)
- (7)
- (11)
- (1)
- (2)
- (1)
- (1)
- (1)
- (13)
- (12)
- (4)
- (6)
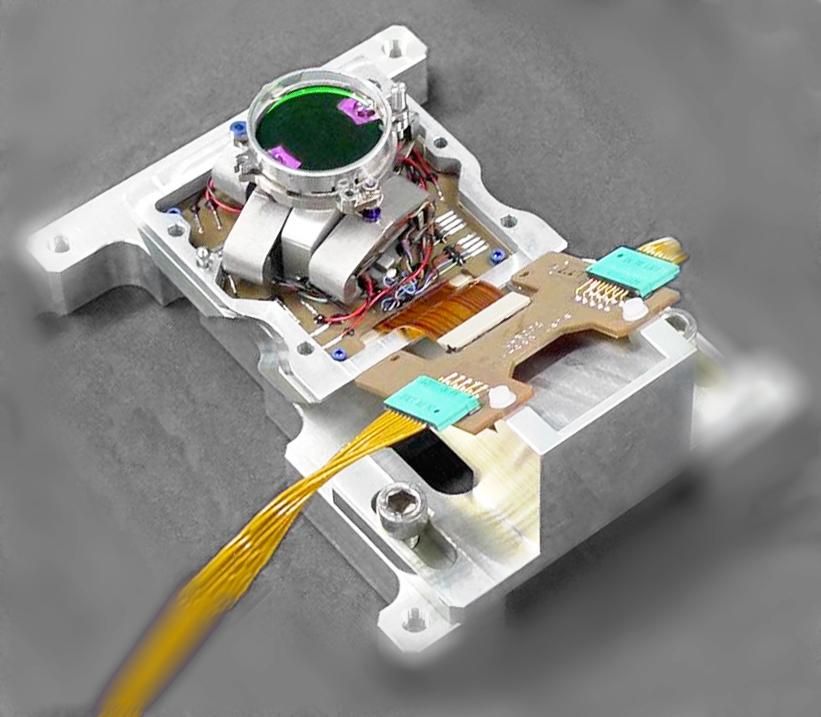
ATLID BSA Beam steering assembly piezo tip tilt
19 June 2023
ATLID (ATmospheric LIDar) is one of the four instruments of EarthCARE satellite, it shall determine vertical profiles of cloud and aerosol physical parameters such as altitude, optical depth, backscatter ratio and depolarisation ratio. The BSA (Beam Steering Assembly), included in emission path, aims at deviating a pulsed high energy UV laser beam to compensate the pointing misalignment between the emission and reception paths of ATLID [1]. It requires a very high stability and high resolution.
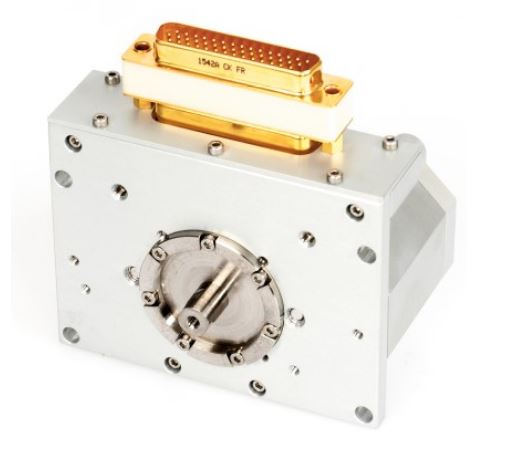

Beam splitter mechanism actuator for IASI NG
3 September 2020
The Infrared Atmospheric Sounding Interferometer New Generation (IASI-NG) is a key payload element of the second generation of European meteorological polar-orbit satellites (METOP-SG) dedicated to operational meteorology, oceanography, atmospheric chemistry, and climate monitoring.
Recent advances in active damping and vibration control
6 January 2002
This paper reviews some concepts used for active vibration control and vibration isolation. It is divided into two parts. Part 1 reviews some control strategies based on collocated control systems, which offer promising results for space and civil engineering applications. Part 2 (starting at section 4) is focused on automobile applications.

Beam steering mechanism for earthcare atmospherice Lidar Instrument: an improved piezo tip-tilt mechanism
19 June 2023
In the context of the ATLID instrument [1] embedded in the EarthCARE mission (Earth Cloud, Aerosol and Radiation Explorer), a Beam Steering Assembly is deviating a pulsed high energy UV laser beam to compensate the pointing misalignment between the emission and reception paths of ATLID with a very high stability and high resolution. Within the EarthCARE mission, led by ESA, Astrium is responsible for the ATLID instrument. The BSA development, manufacture and tests were assigned by Astrium to Sodern, an EADS filial.

Beam steering mirrors: from space applications to optronic applications
19 June 2023
Fast growing Laser and new optic applications drive more and more needs for beam steering mirrors (BSM) and Fast Steering Mirror (FSM). For space optic instruments, CEDRAT TECHNOLOGIES has developed for 20 years several piezoelectric tip-tilt mechanisms. Presented recent examples include the ATLID BSA small tit tilt for quasi static nano pointing and MEFISTO, a large tit tilt for fast micro positioning. These space mechanisms perform high precision functions while being compact, lightweight and resistant to external vibrations and shocks. As shown in the paper, these advantages allow these technologies addressing several needs for other optronic applications than space, such as active stabilisation, micro scanning, disturbance compensation in IR imagers or telescopes.

BRUCE – Electromagnetic Actuated Pin Puller
12 January 2012
Pin pullers are used to hold, lock or secure deployable or moving parts on spacecrafts during their launching. These ‘one shot’ actuators used to be based on explosive charges. Pin pullers important characteristics are their retraction force that needs to be sufficient to pull the pin out of the locking mechanism, their maximum radial force, which limits the size of the secured system, and their dimensions and weight. The possibility of resetting the mechanism is also an appreciated advantage. Upon request of CNES, the French National Space Agency, CEDRAT TECHNOLOGIES has designed a resettable electromagnetic actuated pin puller, called BRUCE


