Publications
Categories
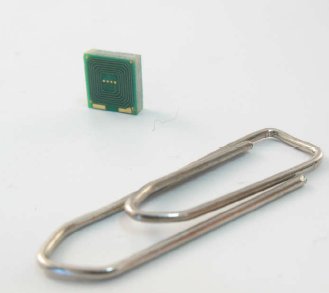
Eddy current sensors on Printed Circuit Board for compact mechatronic application
19 June 2023
In a contact of always smaller and smarter mechatronics devices, the needs of more integrated sensors becomes critical. Particularly, small mechanisms using small actuators like piezo actuators require compact sensors, with performances that measure up to the actuators characteristics.

Investigations on a directly coupled piezoactuated tool feed system for micro electro discharge machine
19 June 2023
A directly coupled piezoactuated tool feed mechanism is proposed and a prototype micro-electrodischarge machine (micro-EDM) is developed. The piezoactuator is used to feed the tool and also to sense the tool displacement from a reference position. The hysteresis behavior of the piezoactuator is also incorporated through an electromechanical model for estimating the actual tool displacement. Simulation results for piezoactuator displacement are compared with the experiment and a maximum error of 15% was observed. Further, in order to control the tool feed rate during machining, a tool feed controller based on the gap voltage feedback is developed.

Semi-passive vibration control technique via shunting of Amplified Piezoelectric Actuators
12 January 2016
The objective of this paper is to provide results of an experimental and analytical investigation of Amplified Piezoelectric Actuators (APA) as vibrational isolator in a configuration of a mechanical Single Degree of Freedom system. The investigation is aimed at assessment of the mechanical properties modification ability via shunting techniques. The investigation consist of a phenomenological modelling of the APAs considered as generators and experimental verification of the vibrational energy dissipation ability in frequency domain. The results obtained during this investigation reveal that it is feasible to receive more than 20 dB reduction of the displacement amplification in the resonant range. Moreover, three tested examples of APA reveal up to 9 % of resonant frequency shift due to proper adjustment of the electronic shunting circuit, which is an encouragement for further analyses towards application of the APAs in semi-passive vibration control applications.
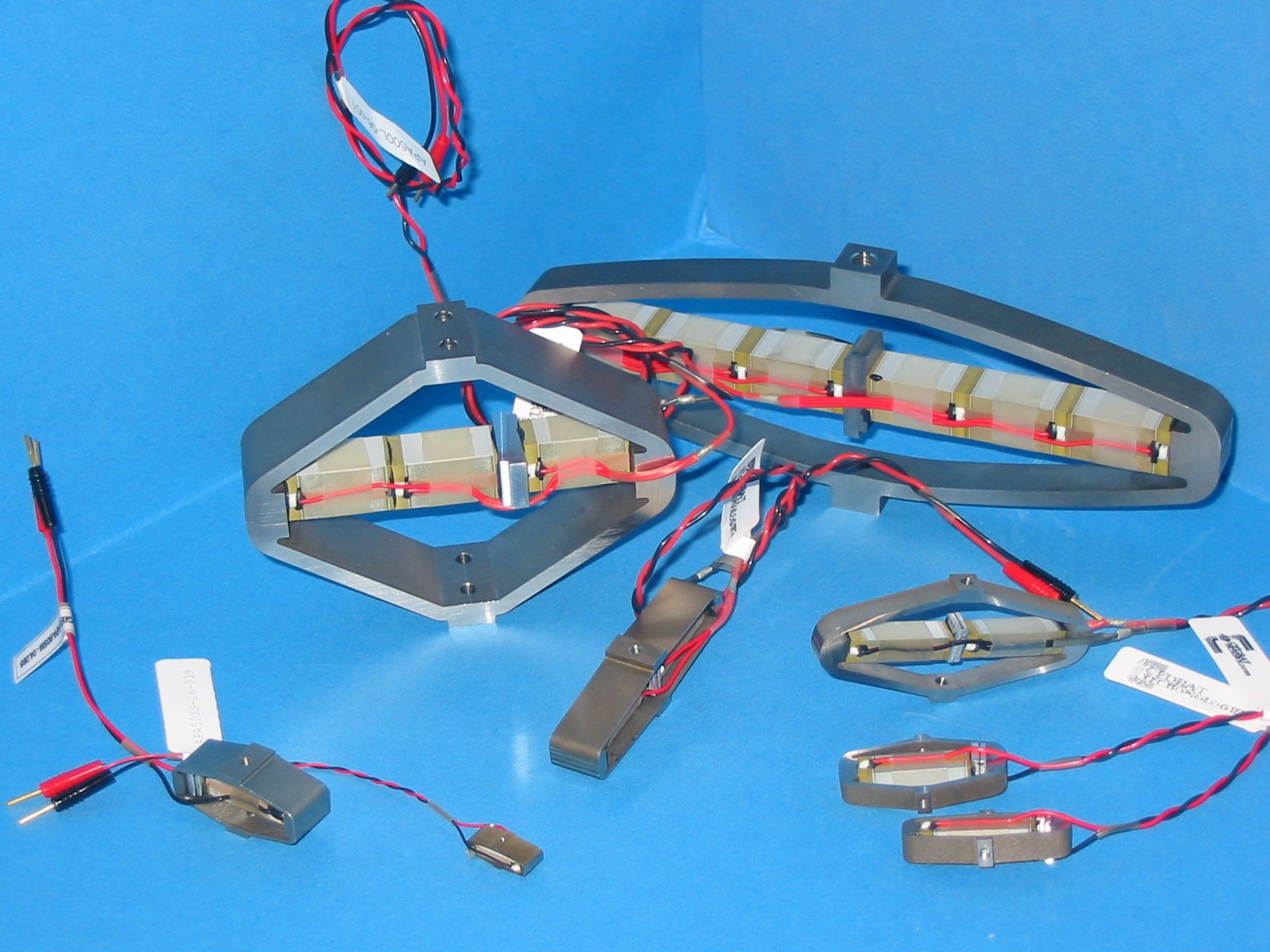
Actionneurs piezoélectriques pour positionnement rapide et précis
19 June 2023
Several classes of low voltage piezo actuators have been developed by CEDRAT TECHNOLOGIES to cover precise positioning needs and / or fast. This paper discusses the ability of these actuators to cover these needs and illustrates this through
various applications (mechanisms, shock absorbers, valves) in the fields of instrumentation, space, aeronautics and automotive.

Very Compact Integration of an Ultra-Low Vibration Platform for Space Cryocoolers Using Miniature High Frequency Actuators
19 June 2023
Air Liquide advanced Technologies in collaboration with Cedrat Technologies and SMAC has performed a study of a compact vibration control platform for mechanical cryocoolers. This solution has been proposed as an alternative approach to cryocooler integration with respect to suspended systems that must be mechanically locked during the launch phase. This system allows significant reduction of the platform’s physical size and mass.
Comparison of Viscoelastic Property Characterization of Plastisol Phantoms with Magnetic Resonance Elastography and High-Frequency Rheometry
7 November 2019
This study aims at evaluating Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE) as a reliable technique for the characterization of viscoelastic properties of soft tissues. Three phantoms with different concentrations of plastisol and softener were prepared in order to mechanically mimic a broad panel of healthy and pathological soft tissues. Once placed in a MRI device, each sample was excited by a homemade external driver, inducing shear waves within the medium. The storage (G’) and loss (G’’) moduli of each phantom were then reconstructed from MRE acquisitions over a frequency range from 300 to 1,000 Hz, by applying a 2D Helmholtz inversion algorithm. At the same time, mechanical tests were performed on four samples of each phantom with a High-Frequency piezo-Rheometer (HFR) over an overlapping frequency range (from 160 to 630 Hz) with the same test conditions (temperature, ageing). The comparison between both techniques shows a good agreement in the measurement of the storage and loss moduli, underlying the capability of MRE to noninvasively assess the complex shear modulus G* of a medium and its interest for investigating the viscoelastic properties of living tissues. Moreover, the phantoms with varying concentrations of plastisol used in this study show interesting rheological properties, which make them good candidates to simulate the broad variety of viscoelastic behaviors of healthy and pathological soft tissues.


