Publications
Categories

Actuators, transducers and motors based on giant magnetostrictive materials
19 June 2023
Rare earth-iron magnetostrictive alloys, especially Terfenol-D, feature “giant” magnetostrains: static strains of 1000-2000 ppm and dynamic strains of 3500 ppm are reported.
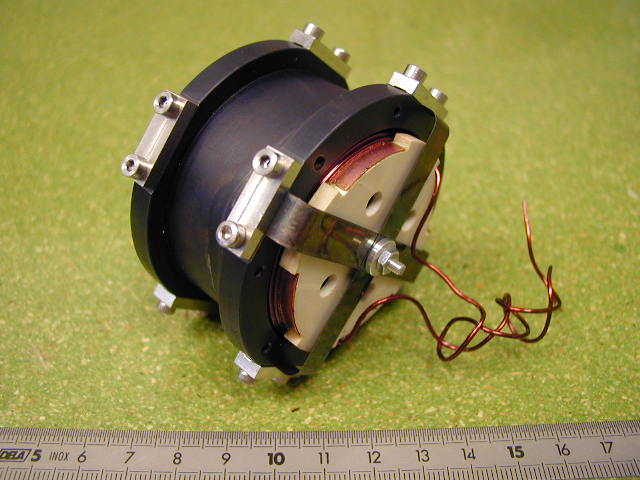
Space compliant mobile voice coil actuator
19 June 2023
A moving coil actuator for high precision positioning and compatible with space technology specifications has been designed and successfully tested. General space technology requirements are the use of no degassing material, no lubrication, low mechanic time constant, low electrical power consumption, and thermal energy evacuation through radiating and conducting exchanges (no convection because of operation in vacuum environment). These specifications have been accounted in the design, the realisation and the test of a successful prototype: Thanks to a good design of thermal drains, the actuator presents a high force versus weight ratio.

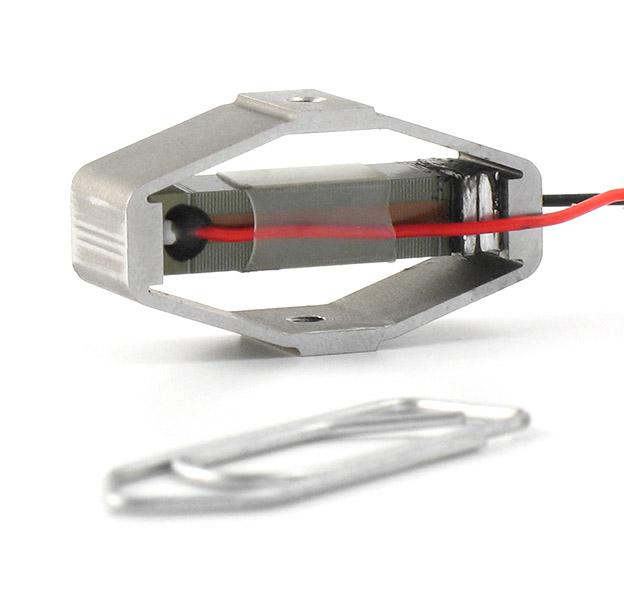
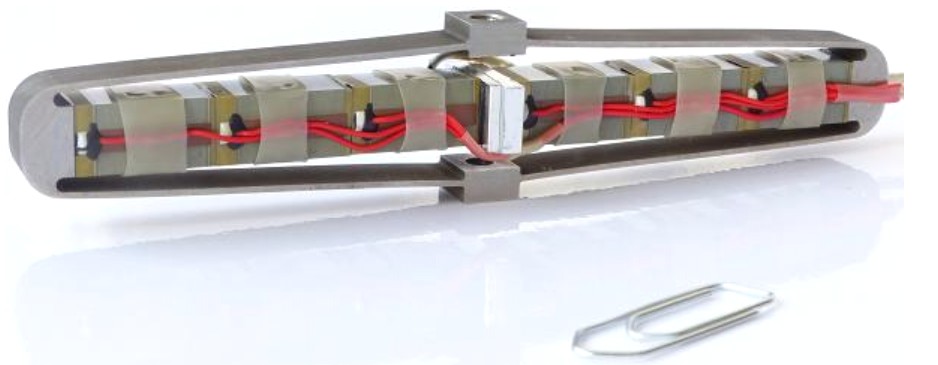
Contactless Position sensors for space mechanisms based on eddy current sensing
19 June 2023
For more than 20 years, CTEC has been involved in various space missions, delivering products designed for severe environment conditions (vibrations, shocks, vacuum, humidity, wide thermal range including cryogenic). Eddy current sensor (ECS) technology, using printed circuit board (PCB) for printed coils, provides both a good resolution/accuracy and a good robustness against temperature variations.These sensors are available commercially off the shelf (COTS).
Fast tomoelastography of the mouse brain by multifrequency single shot MR elastography
7 November 2019
To introduce in vivo multifrequency single-shot magnetic resonance elastography for full-FOV stiffness mapping of the mouse brain and to compare in vivo stiffness of neural tissues with different white-to-gray matter ratios.
Brain mechanical properties influence many vital neurological functions including brain development, metabolism, and tissue repair. However, studying brain mechanical properties in a noninvasive fashion encounters a number of challenges including the fact that the brain is protected by the skull as well as the heterogeneous and complex geometry of the brain. At present, magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) is the sole modality allowing noninvasive measurement of in vivo brain mechanical properties in patients and small animals.

Space Tribometers: Design for Exposed Experiments on Orbit
12 March 2012
Eight pin-on-disk tribometers have been made for testing materials in space on board the International Space Station. They will be exposed directly to the low earth orbit (LEO) environment on board the ‘‘Materials on the International Space Station Experiments’’ platform where they will experience extreme conditions including atomic oxygen, ultrahigh vacuum, radiation (including UV radiation), and thermal ranges from -40 to 60 C.
Advantages of large piezo actuators and high power drivers for fatigue and fretting test
19 June 2023
Constant expansion of new materials requires fretting or fatigue machines in order to test their failure. In many cases tests must be performed in severe conditions and at high frequency. These requirements come from the use of the materials in highly demanding applications. At the same time it is expected to reduce the time required to characterise such materials. Piezoelectric actuators are more and more common in testing machines, but they still reach limitations in terms of maximum displacement, cycling frequency or power. In order to cope with these issues, Cedrat Technologies has been investigating solutions. In this paper long stroke and high frequency actuators, coupled with powerful driving control are introduced. These actuators are based on piezoelectric materials and can be easily integrated into the fatigue machines. In order to improve precision of these tests, two of the most common displacement sensors used in smart actuators are also presented in this paper.


