Publications
Categories
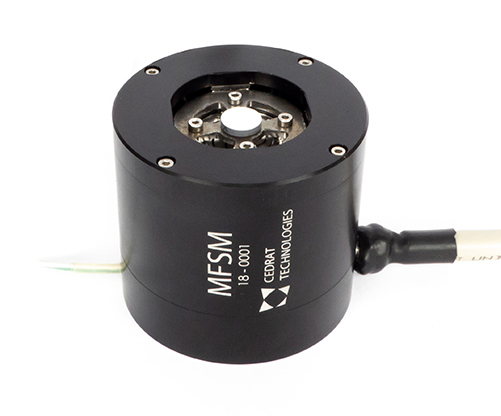

Large Stroke Fast Steering Mirror for Space Free-Space Optical communication
2 March 2020
Free-Space Optics and Deep Space Optical Communication request new compact low-power high-stroke high-bandwidth Fast Steering Mirrors. To address this need, CEDRAT TECHNOLOGIES has developed a Magnetically-actuated Fast Steering Mirror called M-FSM, taking heritage of its MICA™ technology. This mechanism offers Rx Ry strokes larger than +/-2° with a 250Hz bandwidth when tilting a 10mm-diameter mirror. Closed loop control is achieved using integrated eddy current sensors. Requested power is reduced leading to low heating and allowing high duty cycle. Vibration tests allow to define first limits and conditions for the M-FSM to bear external vibrations.
ACTUATOR2008 Stepping piezoelectric actuators Abstract
19 June 2023
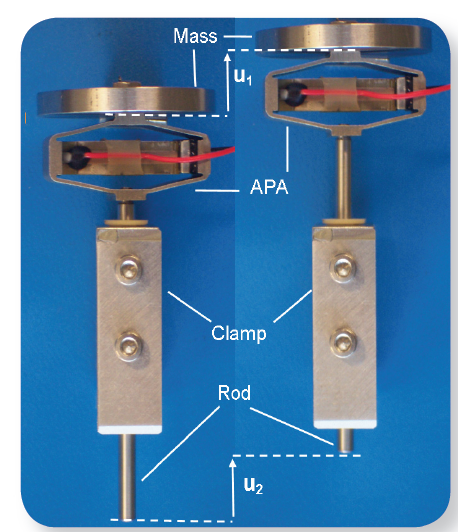
Stepping Piezoelectric Actuators (SPA) are new long-stroke linear piezoelectric motors for micro/nano positioning applications benefiting of the advantages and the heritage of the APA. SPA are formed of only 4 parts: the well-established Amplified Piezoelectric Actuators (APA), a front mass, a clamp and a rod.
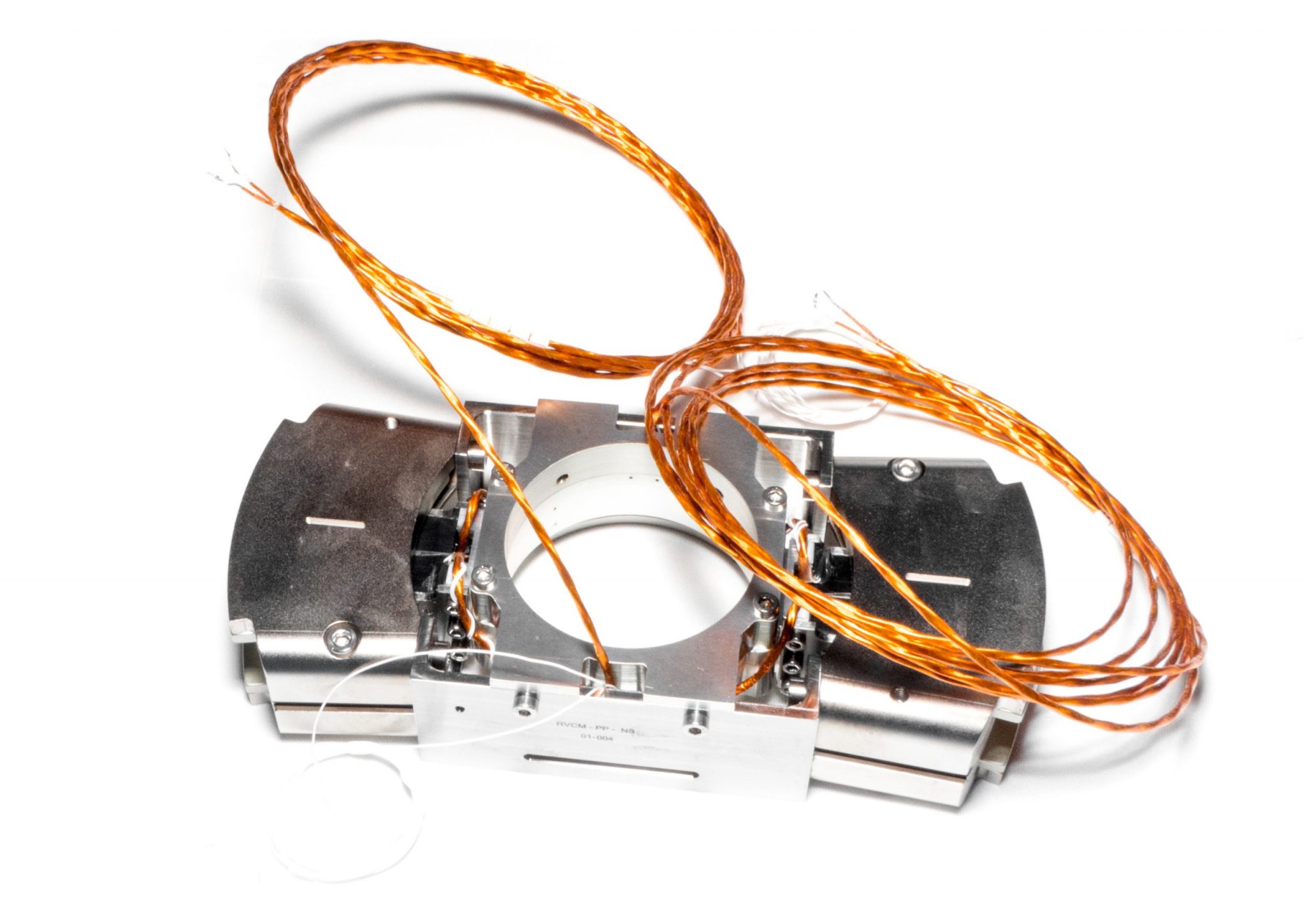
Large stroke Rotary Voice Coil Motor for cryogenic application
19 June 2023
CTEC is developing and testing Rotary Voice Coil Motors (RVCM) for new cryogenic space scan mechanisms applications,
based on former MTG space program heritage. The RVCM is an electromagnetic motor based on Laplace force.
The motor is composed of coils at the rotor part (mobile) and magnets at the stator part (fixed). The Laplace motor
generates a pure torque, without cogging or parasitic force drawback, which makes it specifically relevant for scan mechanisms.
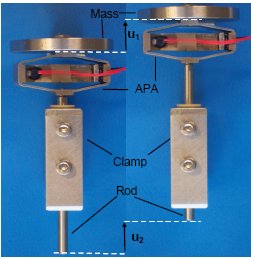
ACTUATOR2008 Stepping piezoelectric actuators based on APA®
1 January 2008
Abstract:
Stepping Piezoelectric Actuators (SPA) are new small long-stroke linear piezoelectric motors for micro/nano positioning applications benefiting of the advantages and the heritage of the APA. SPA is formed of only 4 parts: the well-established Amplified Piezoelectric Actuators (APA), a front mass, a clamp and a rod. SPA operates by accumulation of small steps, using inertial mode, impact forces and stick-slip effects, allowing performing long strokes (> 10mm). Main advantages induced by the choice of the APA above a usual inertial drive mechanism (IDM) are high reliability, low peak current ( 20mm/s), useful forces (from 1N for XS to 30N for SM type) and nano positioning mode.

ACTUATORS BASED ON GIANT MAGNETOSTRICTIVE MATERIALS
6 January 2002
Magnetic field induced strain materials are classically represented by Giant Magnetostrictive Materials (GMM) such as Tb-Dy-Fe alloys offering magnetostrain of 0.1-0.2%. This family of smart materials has been extended for some years by cryogenic magnetostrictive materials such as Td-Dy and (Tb1-xDyx)Zn offering magnetostrain of 0.2- 1%. Even more recently, it has been completed by new Magnetic Shape Memory Materials (MSM) such as Ni-MnGa offering magnetostrain of 2-6%. These materials have lead to quite various large stroke and large force actuators. Some of these actuators meet the requirements of applications in different fields such as space or machine tools. The object of this paper is to review the present situation and recent progresses in the field of magnetic field induced strain materials, actuators, modelling and applications, including commercial aspects.
LDIA2007 Moving coil or moving iron controllable actuators
19 June 2023
There is a strong demand of controllable actuators for both traditional and new applications. A controllable actuator should be able to accelerate, break, inverse the motion of the load, all along the stroke. It means the force produced by the actuator should be proportional (at least roughly) to the applied electric excitation, and in particular, the sign of the actuation force could be changed all along the stroke.


