Publications
Showing 103–108 of 213 results
-

Active control of vibrations of a space truss using amplified piezoelectric actuators
0,00 € Add to downloads -

Active damping of vibrations applied on ski structures
0,00 € Add to downloads -

Fast and fine Steering Mirrors based on piezoelectric & magnetic actuator technologies for Air and Space
0,00 € Add to downloads -

Active flap device for helicopters based on Cedrat Amplified Piezoelectric Actuators
0,00 € Add to downloads -
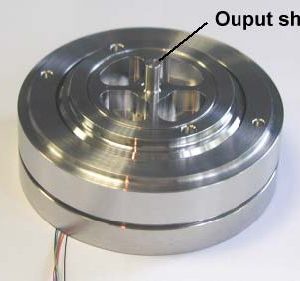
Rotating piezoelectric motors for high precision positioning & space applications
0,00 € Add to downloads -

Ski embbeded piezo system
0,00 € Add to downloads


