Publications
Showing 91–96 of 213 results
-
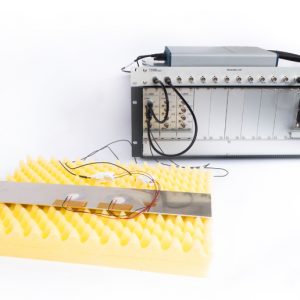
Robustness of SHM techniques based on lamb waves
0,00 € Add to downloads -

XY200M a new design of piezo stage
0,00 € Add to downloads -

Experimental assesment and further development of amplified piezo actuators for active flap devices
0,00 € Add to downloads -

Rosetta Midas Stage Atila space applications
0,00 € Add to downloads -
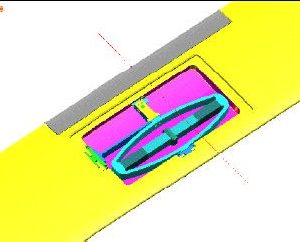
Experimental assessment of an active flap device
0,00 € Add to downloads -

Extreme performance of piezo system: High stroke, high frequency, high temperature
0,00 € Add to downloads


