Publications
Categories
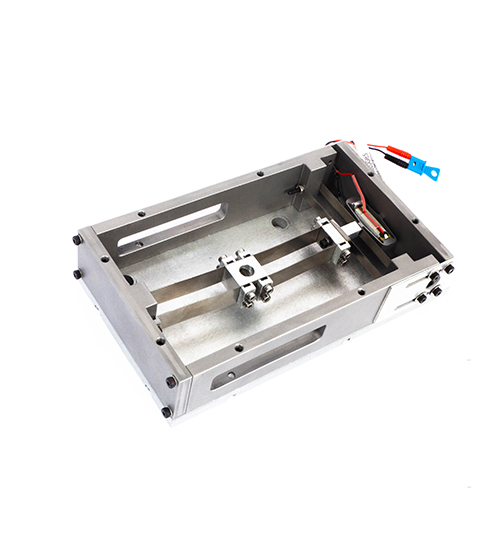

A wideband vibration energy harvester with integrated energy management designed for harsh environment.
14 June 2024
Bistable energy harvesters (BEH) are well adapted devices to deal with the variation of the vibration source frequency spectrum. Indeed, the non-linear motion of this kind of harvester allow to reach a harvesting bandwidth up to 50% of the resonant frequency compared to 1-2% of the resonant frequency typically for conventional linear energy harvesters. CEDRAT TECHNOLOGIES proposes a design using buckled beam and Amplified Piezoelectric Actuator (APA®) technology based on an architecture patented by the USMB. The nonlinear behavior of such a kind of energy harvester has already been studied in the literature and has demonstrated promising results.
Due to the use of buckled beam, the bistable energy harvester is very sensitive to the thermal expansion resulting from the harsh environment. In this paper, it is proposed an improved design to manage the thermal expansion and ensure harvesting capabilities on a wide temperature range from -40°C to +80°C.
Furthermore, an electronic extraction circuit has been implemented to deliver a regulated output voltage to power an IoT. Moreover, this electronic circuit can deal with spontaneous excess of energy by storing it into a supercapacitor or a battery and sink this energy to still powering the IoT when the vibration level decrease. The BEH with the electronic extraction circuit can generate a power of 8mW.
The combination of an athermalized Bistable Energy Harvester with an electronic extraction circuit increases the technological readiness level to be integrated in system subjected to harsh environment like railway application for instance.
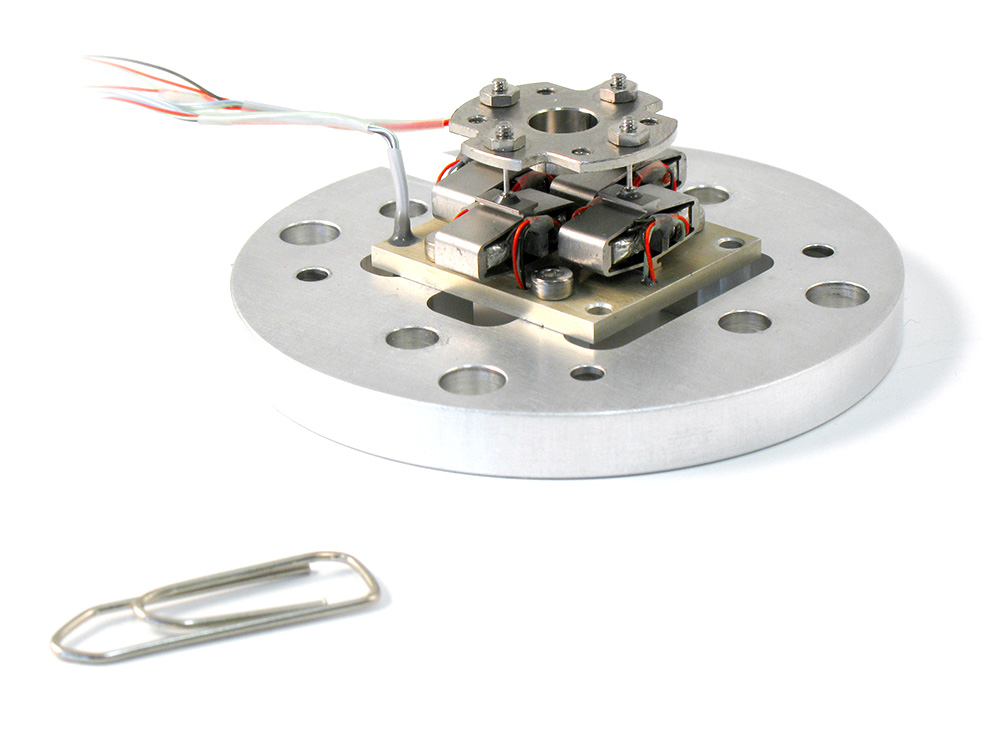
Design and testing challenges of space piezoelectric pointing mechanisms as mirror mass increases
4 December 2025
Piezoelectric pointing mechanisms should not only perform high precision functions but should also be extremely resistant while remaining compact and lightweight to withstand the space launch requirements. Ensuring the vibration test success, still without using any launch lock, is a critical aspect of the projects.
This paper presents how the increase of the mechanism stroke and the payload size is affecting the capability of the devices to support vibrations during launch, and how the non-linear behaviour of the piezoelectric ceramic stiffness may affect the shaker’s drive control during qualification tests, which can lead to significant over-testing.
Finally, recommendations are provided that can be applied when selecting testing equipment, based on Cedrat Technologies experience.
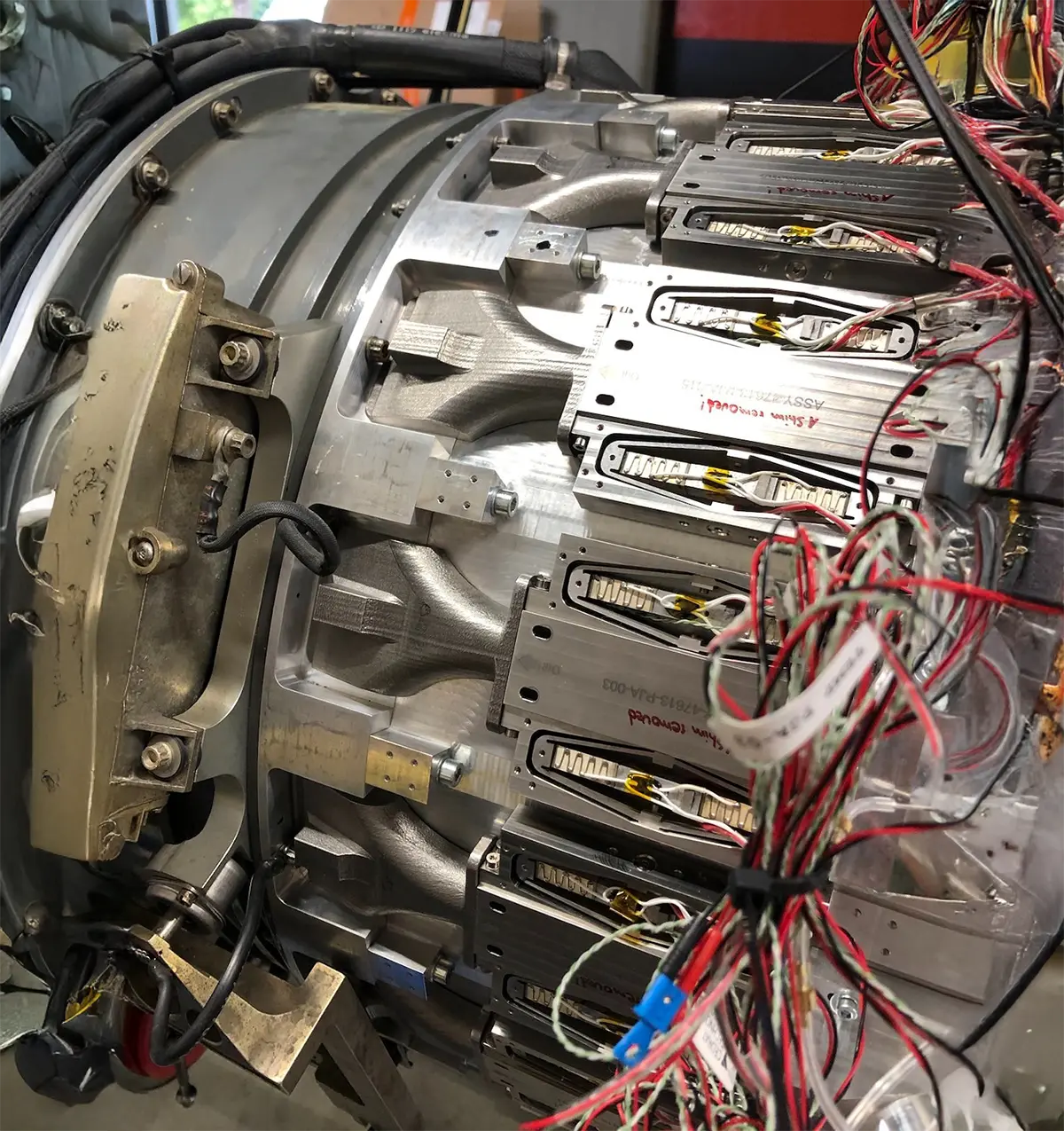

Effects of Tip Injection on a Turbofan Engine with Non-Invasive High-Speed Actuators
27 May 2025
New piezoelectric actuators were designed and manufactured with a new engine inlet for the Larzac 04 C5 jet engine. It has noninvasive injection positions that do not have any measurable effect on the inlet air flow when it is switched off. The main focus of the system design was to achieve high power of the injected air and, as a result, a high SMI. The results presented enable a maximum SMI of 99%. A variety of engine operating conditions and injection positions were experimentally tested and discussed regarding SMI. Additionally, the complex relationship between SMI gains and thrust specific fuel consumption (TSFC) is explored in a power balance analysis, revealing a trade-off between SMI improvement and increased energy consumption.
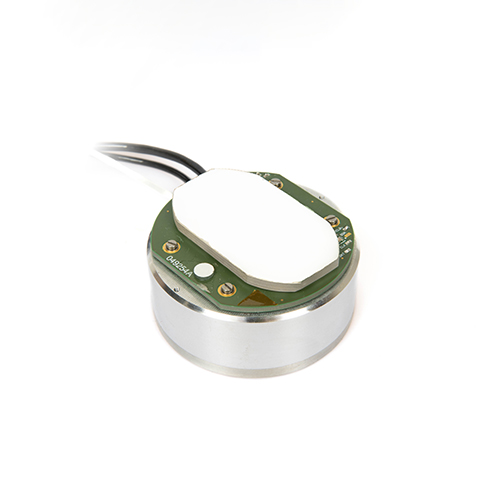

Improving dynamic accuracy of closed loop bandwidth of piezo mechanisms with advanced control laws and embedded eddy current position sensors
14 June 2024
Fast Steering Mirrors (FSM) play an important role in diverse optical applications for beam stabilization, image sharpening or dynamic beam steering. These applications require the FSM to have a precise response across a large frequency range, thus the need of a dynamic controller. But the controller is ultimately limited, among other factors, by the performance of the sensor: its ability to measure accurately the required physical value and with a sufficient bandwidth. The compact, dynamic and precise embedded Eddy Current Sensors (ECS) developed by Cedrat Technologies, combined with a model-based controller allow a two and a half times improvement on the bandwidth compared to current sensing technology, while being more precise overall.
In-situ monitoring of μm sized electrochemically generated corrosion pits using Lamb waves managed by a sparse array of piezoelectric transducers
2 December 2024
Corrosion is a major threat in the aeronautic industry, both in terms of safety and cost. Efficient, versatile, and cost affordable solutions for corrosion monitoring are thus needed. Ultrasonic Lamb Waves (LW) appear to be very efficient for corrosion monitoring and can be made cost effective and versatile if emitted and received by a sparse array of piezoelectric elements (PZT). A LW solution relying on a sparse PZT array and allowing to monitor μm-sized corrosion pit growth on stainless 316L grade steel plate is here evaluated. Experimentally, the corrosion pit size is electrochemically controlled by both the imposed electrical potential and the injection of a corrosive NaCl solution through a capillary located at the desired pit location. In parallel, the corrosion pit growth is monitored in-situ every 10 s by sending and measuring LW using a sparse array of 4 PZTs bonded to the back of the steel plate enduring corrosion. As a ground truth information, the corrosion pit volume is estimated as the dissolved volume balancing the electronic charges exchanged during corrosion. The corrosion pit radius is additionally checked post-experiment precisely with an optical measurement. Measured LW signals are then post-processed in order to compute a collection of synthetic damage indexes (DIs). After dimension reduction steps, obtained DI values correlates extremely well with the corrosion pit radius. Using a linear model relating those DI values to corrosion pit radius, it is demonstrated that corrosion pit from 30 μm to 150 μm can be reliably detected, located, and their upcoming size extrapolated. Two independent experiments were achieved in order to ensure the repeatability of the proposed approach. LW managed by a sparse PZT array thus appears to be reliable and efficient to monitor growth of μm-sized corrosion pits on 316L steel plates. If embedded in aeronautical structure, such an approach could be a versatile and cost-effective alternative to actual non-destructive maintenance procedures that are time and manpower consuming.
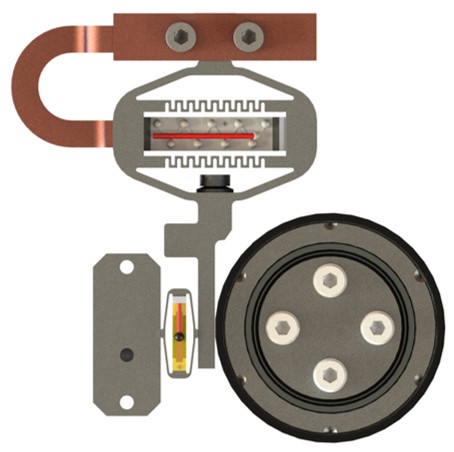
Inertial & Inchworm piezoelectric motors: Design and Motorization selection key aspects
14 June 2024
Piezoelectric motors have gained increasing prominence in various applications due to their unique capabilities and advantages. These motors are adapted for applications which require non-magnetic and radiation compatibility, high force/volume ratio, good unpowered stall force and low power consumption. Cedrat Technologies (CTEC) have developed inertial and inchworm motorization for a wide range of application such as Space, Defense and Nuclear. Each motorization solution has its own advantages and disadvantages which are discussed in this paper. Key aspect for the design and key element for the motorization selection are presented below.


